| Metrics | Logs | Traces | Telemetry Pipeline Agent |
|---|---|---|---|
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | v1.46.0+ |
The Parse XML Processor is utilized to parse XML document strings from specified fields within log, metric, or trace data. It’s particularly useful when your telemetry data contains a serialized XML document, and you need to convert them into a structured format for easier analysis and filtering. The processor supports specifying the source field and the target field for the parsed XML data, offering flexibility in handling diverse data structures.
When dealing with telemetry data that includes an XML document embedded within logs, metrics, or traces, the Parse XML Processor becomes instrumental. For instance, logs from certain applications or systems might contain XML documents representing specific attributes or metadata. By utilizing the Parse XML Processor, these XML documents can be parsed and converted into structured data, enhancing readability and facilitating more complex queries and analyses.
The parsed XML is structured as follows:
content field.tag field.attribute field.children field.As an example, see the following XML:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<Log>
<User>
<ID>00001</ID>
<Name type="first">Joe</Name>
<Email>joe.smith@example.com</Email>
</User>
<Text>User fired alert A</Text>
</Log>
This XML, when parsed, becomes:
{
"tag": "Log",
"children": [
{
"tag": "User",
"children": [
{
"tag": "ID",
"content": "00001"
},
{
"tag": "Name",
"content": "Joe",
"attributes": {
"type": "first"
}
},
{
"tag": "Email",
"content": "joe.smith@example.com"
}
]
},
{
"tag": "Text",
"content": "User fired alert A"
}
]
}
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Telemetry Type | The type of telemetry to apply the processor to. |
| Condition | The condition to apply the XML parsing. It supports OTTL expressions for logs, metrics, and traces. This field determines which telemetry data entries are processed based on their content and attributes. |
| Source Field Type | Determines the type of source field for logs, metrics, or traces. This can be Resource, Attribute, Body, or Custom for logs and Resource, Attribute, or Custom for metrics and traces. It defines where the processor should look to find the XML document to parse. |
| Source Field | Specifies the exact field where the XML document is located, based on the selected Source Field Type. For instance, if the Source Field Type is Attribute, this field should specify the particular attribute containing the XML document. |
| Target Field Type | Like the Source Field Type, this field determines the type of target field for logs, metrics, or traces where the parsed XML data will be stored. The options are similar, allowing users to store the parsed data as a resource, attribute, body, or in a calculated field. |
| Target Field | Specifies the exact field where the parsed XML data will be stored, based on the selected Target Field Type. This allows users to organize and structure the parsed data in a manner that facilitates easy querying and analysis. |
In this example, we have a basic log that details an action and the user that triggered the action, like an audit log. This log is in XML format, and we’d like to parse the content into a structured log.
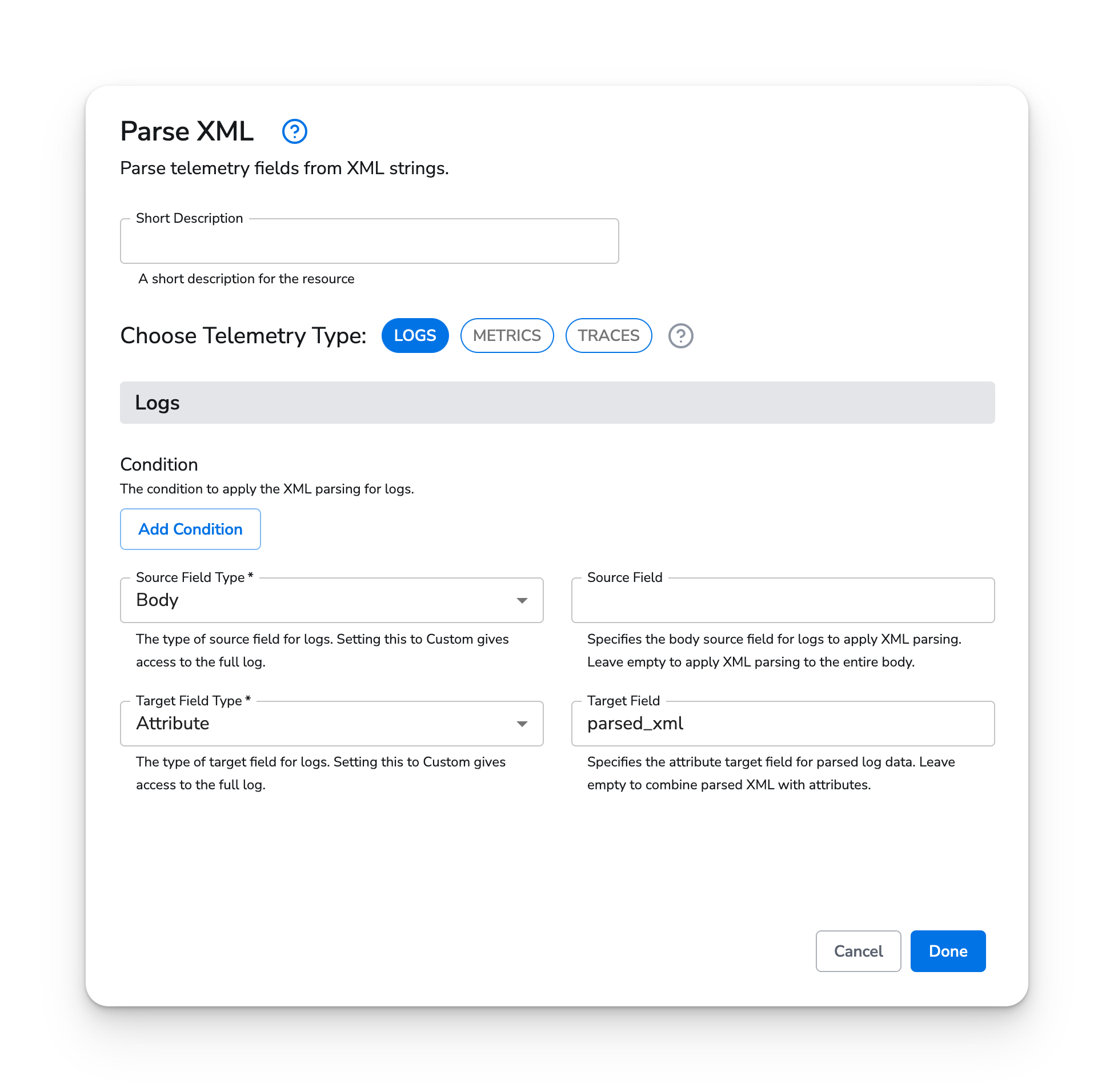
Here is a sample log record:
{
"body": "<Log><User><ID>00001</ID><Name><First>Joe</First></Name></User><Text>User did a thing</Text></Log>"
}
In order to parse the body of the log record, and store it on the parsed_xml attribute, we can configure the Parse XML processor as follows:
LogstrueBodyAttributeparsed_xmlAfter parsing, the log record looks like this:
{
"body": "<Log><User><ID>00001</ID><Name><First>Joe</First></Name></User><Text>User did a thing</Text></Log>",
"attributes": {
"parsed_xml": {
"children": [
{
"children": [
{
"content": "00001",
"tag": "ID"
},
{
"children": [
{
"content": "Joe",
"tag": "First"
}
],
"tag": "Name"
}
],
"tag": "User"
},
{
"content": "User did a thing",
"tag": "Text"
}
],
"tag": "Log"
}
}
}