Ask questions about your telemetry data in natural language.
Canvas combines conversational AI with interactive visualizations to help you analyze observability data, understand system behavior, and troubleshoot issues within Honeycomb. Ask questions in natural language, and Canvas queries your data and displays results visually.
Canvas is an AI-guided workspace that translates natural language questions into queries, runs them against your data, and presents results through interactive visualizations. Unlike traditional query building, Canvas maintains context throughout your investigation, letting you ask follow-up questions and refine your analysis conversationally.
Use Canvas to:
Canvas combines AI-powered query generation with Honeycomb’s core capabilities to support conversational investigation.
Canvas integrates directly with Honeycomb’s query engine and has access to:
Canvas translates natural language requests into structured queries using Honeycomb’s API and presents results in an accessible format with appropriate visualizations.
Canvas understands references to your Datasets, Environments, and fields. It can also link to existing queries and traces, making it easier to explore complex questions without switching between multiple tools.
Canvas makes all generated queries available throughout your investigation. You can examine the exact query syntax Canvas creates from your natural language questions and modify queries directly in the Query Builder.
Canvas auto-saves investigations as persistent workspaces that you can revisit and share with Team members.
Canvas operates within strict security boundaries to protect your data.
Canvas:
Additionally, you can choose whether to share your individual Canvas investigations with your team or keep them private.
Begin an investigation by creating a new Canvas or opening an existing query to use as context in Canvas.
To start a new Canvas investigation:
To open an existing query in Canvas:
Reference specific Datasets, Environments, or fields in your prompts using mentions (@).
You can also include links to queries.
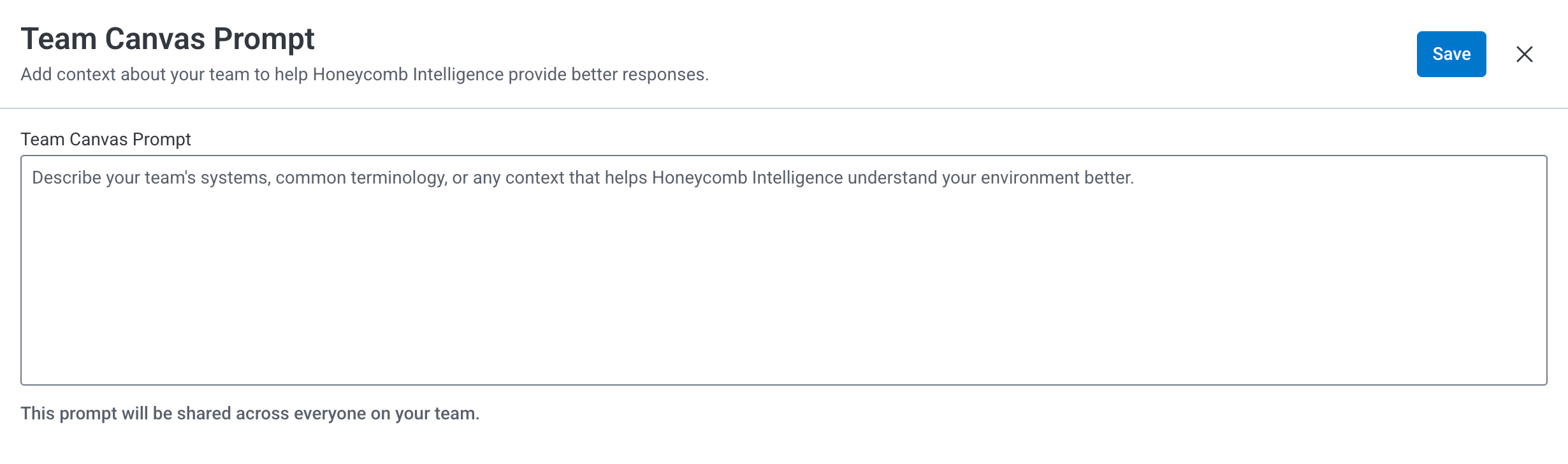
Team owners can add custom context that is included in every prompt sent to Canvas by their teammates.
To add team-level custom context:
Use these examples as starting points to explore what’s possible in Canvas:
/link/to/a/trace/”@my_dataset based on fields prefixed with my_prefix?”frontend dataset?”production and staging.”Why did service X have high latency at 2pm yesterday?How does the error rate in production compare to staging?Show me the pattern of database connections over the last week.Is there a relationship between cache miss rate and API latency?Canvas displays the queries it generates from your natural language questions in visualization panels alongside your chat session.
Interact with Canvas visualizations the same way you would with Query Results:
Each visualization panel includes options to examine the query syntax:
Both options open the query in Query Builder, where you can modify it to refine results.
Share individual queries from a Canvas investigation by selecting the link icon () on any query panel. This copies a shareable link to that specific query.
You can generate a shareable link to your Canvas investigation, so you can share it with your Team.
To share a non-private Canvas, select Share ().
Control who can access your Canvas investigation by setting its privacy level.
Canvas investigations default to Shared with my team (), making them visible to all Team members.
To create a private investigation that only you can access, select Private to me () from the privacy dropdown.
You can change the privacy setting at any time during your investigation.
Canvas automatically saves your investigations as named, persistent workspaces that can be revisited. To return to a previous investigation, select it from the Recent investigations section on the Canvas entry page.
Follow these guidelines to get the most accurate and relevant results from Canvas.
@) to reference specific Datasets, Environments, or fields.Canvas works within these boundaries:
If Canvas doesn’t respond as expected, try these troubleshooting steps.
Canvas needs accurate Dataset names and proper permissions to access your data.
If Canvas reports it can’t find a Dataset:
Query parameters like time range and filters determine whether Canvas finds matching data.
If Canvas returns no results:
Like all AI tools, Canvas may not always provide the exact answer you need. If Canvas makes a mistake or doesn’t understand your question, try these approaches:
@) to specify Datasets, Environments, or fields.